Datasheet 搜索 > MOS管 > Infineon(英飞凌) > BSC028N06NS 数据手册 > BSC028N06NS 开发手册 3/37 页

¥ 2.646
BSC028N06NS 开发手册 - Infineon(英飞凌)
制造商:
Infineon(英飞凌)
分类:
MOS管
封装:
PG-TDSON-8
描述:
INFINEON BSC028N06NS 晶体管, MOSFET, N沟道, 100 A, 60 V, 0.0025 ohm, 10 V, 2.8 V
Pictures:
3D模型
符号图
焊盘图
引脚图
产品图
BSC028N06NS数据手册
Page:
of 37 Go
若手册格式错乱,请下载阅览PDF原文件

1 Introduction
Avalanche (and especially repetitive avalanche) do not necessarily belong to the list of common parameters
considered by a MOSFET manufacturer when developing a new family. The reason for this is quite simple:
avalanche typically occurs when the breakdown voltage (V
BR(DSS)
) of the MOSFET is exceeded, meaning that the
part is being used outside its datasheet specification. Consequently, a designer should make all reasonable
attempts NOT to operate a MOSFET in avalanche.
In some applications with long operating lifetime, such as telecom (AC-DC rectifiers, DC-DC bricks) or server
power supply units, the increasing requirement to comply with standards that impose significant voltage
derating (such as IPC9592B-2012) leads designers in the direction of “zero-avalanche-tolerance”. However,
IPC9592 and other similar standards do not necessarily stipulate any derating guidelines for abnormal
conditions.
Additionally, low voltage drives applications such as forklis and power tools are rarely subject to voltage
derating, due to their short operating lifetime and/or their high loop inductances (L
loop
) that make them more
likely to face high V
DS
spikes and, therefore, avalanche conditions.
Furthermore, due to challenging eiciency requirements, designers of other high performance applications
such as servers -do not confuse with server power supplies- would prefer to use repetitive-avalanche-proof
MOSFETs to avoid having to move to a higher voltage class.
As a result of the high number of ‘special cases’ within the multitude of applications where MOSFETs are used,
ruggedness against avalanche is a key requirement for users that MOSFET manufacturers cannot aord to
ignore during any new technology development. Regarding ‘repetitive avalanche’ in particular, the absence of
any rating within a datasheet does not necessarily mean that it was not investigated during the design phase of
the technology.
In the following sections of this document, we will list key facts about avalanche that any designer should keep
in mind when using industrial and standard versions of Infineon’s OptiMOS
TM
families of MOSFETs. We therefore
focus on OptiMOS
TM
3 and the subsequent families that are all n-channel enhancement mode trench power
MOSFETs. Consequently, other MOSFET families are outside the scope of this document.
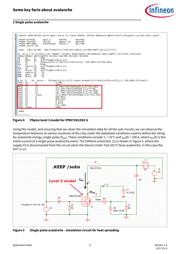
For engineers who do not want to devote too much time to the theory behind avalanche, section 2.1.2 provides
a simulation circuit that can be used to monitor the temperatures at various locations of the MOSFET during
avalanche. Additionally, specific examples are given in sections 3.2.1 and 3.2.2 to allow engineers to assess if a
MOSFET is avalanche safe under their own application conditions. Finally, a formula supplied in section 3.3
assists with rapid computation of avalanche energy when the circuit presents a dierent loop inductance.
Some key facts about avalanche
1 Introduction
Application Note 3 Version 1.0
2017-01-9
器件 Datasheet 文档搜索
AiEMA 数据库涵盖高达 72,405,303 个元件的数据手册,每天更新 5,000 多个 PDF 文件